9.Relation
注意看关系的定义,计数不同性质关系(reflexive,symmetric,antisymmetric)的, 偏序关系
Definition
A binary relation from \(A\) to \(B\) is a subset of \(A\times B\)
The graph of function \(f:A \to B\)is a relation. 但反之不成立
A relation on a set A is a relation from A to A
A relation can be expressed as
- Connection matrix \(m_{ij}=[(a_i,b_j)\in R]\) 可以理解成图的邻接矩阵,只有0和1
- Directed graphs
Properties
| Properties | Definition | Connection Matrix | Digraph |
|---|---|---|---|
| reflexive | \(\forall x\in A,(x,x)\in R\) | 对角线全为1 | 每个结点都有自环 |
| irreflexive | \(\forall x\in A,(x,x)\notin R\) | 对角线全为0 | 每个结点都没有自环 |
| symmetric | \(\forall x,y\in A,(x,y)\in R \to (y,x) \in R\) | \(M=M^T\) | 每一条边都有反向边 |
| antisymmetric | \(\forall x,y\in A,((x,y)\in R\wedge(y,x)\in R)\\ \to x=y\) | 对角线可以为0/1, 非对角线上的对称位置不能同时为1 | 每一条边都没有反向边,可以有自环 |
| asymmetric | \(\forall x \in A,(x,y)\in R\to(y,x) \notin R\) | 对角线全为0,非对角线上的对称位置不能同时为1 | 每一条边都没有反向边,不能有自环 |
| transitive | \(\forall x,y,z\in A ((x,y)\in R\wedge (y,z)\in R)\\ \to(y,z)\in R)\) | \(M^2 \vee M=M\) | 对于每一条从\(u\)到\(v\)长度为2的路径,有一条边\((u,v)\). (即\(R^2\subseteq R\)) |
- 也就是说如果\((x,y) \in R且x\neq y\)则\((y,x)\notin R\) . 如果R是antisymmetric的,那么可以包括(a,a).
A relation can be both symmetric and antisymmetric: \(M=\begin{pmatrix}&1 \ &0\\&0 \ &1 \end{pmatrix}\)
symmectric+transitive=reflexive?
No, for example \(M=0\)
错在symmetric不代表对于任意的\(a\)都存在\(b\)使得\((a,b)\in R\)
Counting relations on set
|A|=n, how many relation on set A is
- reflexive: \(2^{n^2-n}\)
- symmetric: \(\color{red}2^{(n^2-n)/2}\times 2^n=2^{(n(n+1)/2)}\) 注意对角线上可以是0或1
- antisymmetric: \(\color{red}3^{n(n-1)/2}\times 2^n\) 对于矩阵非对角线上的一对对称的元素, 只能是(0,0),(0,1),(1,0). 对角线上可以是0或1
- asymmetric \(3^{n(n-1)/2}\),对角线上全为0
Operations
\(R^{-1}=\{(b,a)|(a,b)\in R \}\)
\(M_{R^{-1}} =M_R^T\)
\(S\circ R=\{(a,c)|(a,b)\in R \wedge \color{red}(b,c)\in S\}\)
注意顺序,S在后面!!!!
对应邻接矩阵的乘法(用与运算代替乘法,或运算代替加法)
\(R^n=R\circ R \circ \dots R\)
或者对应有向图中长度小于等于n的路径(Floyd传递闭包(确信))
The relation R on a set A is transitive if and only if \(R^n \subseteq R\) for n = 1, 2, 3,...
Closures
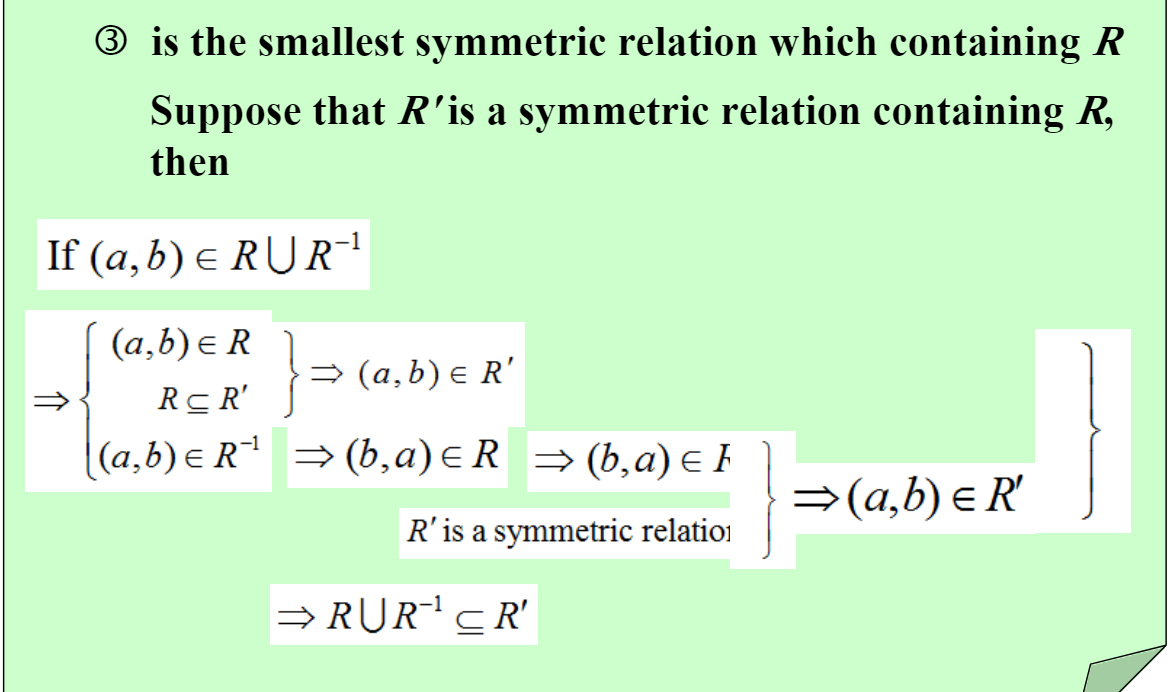
If there is a relation S with property P containing R, such that S is a subset of every relation with property P containing R, then S is called the closure of R with respect to P
证明分3步
-
\(R \subseteq S\)
-
\(S\) 满足性质\(P\)
-
证明S是最小的,可以反证,或者证明任意一个满足P的关系都包含S
reflexive closure: \(R\cup I_a\)
symmetric closure:\(R \cup R^{-1}\)
transitive closure: \(\cup_{i=1}^{\infty} R^i\)
Warshall's Algorithm
手算,每次取第k行和第k列. 用第k列(a[i][k])和第k行a[k][j]两两匹配,如果有2个都是1的,就把a[i][j]设为
Equivalence Relations
reflexive,symmetric and transitive-> equvalence relation
Equivalence class
Equivalence class of \(x\): \([x]_R\) or \([x]\) The set of all elements that are related to an element \(x\)
Eg. \(R=\{(a,b)|a \equiv b\pmod 3\}\)
\([0]=\{3k|k \in Z\},[1]=\{3k+1|k \in Z\},[2]=\{3k+2|k \in Z\}\)
Partitions of a set and Relations
Theorem
左推右很好证。考虑右推左
\(R=\{(a,b)|a,b \in A_i\}\) \(pr(A)=A_1,A_2\dots A_n\)
- reflexive: \(\forall a \in A,\existssss A_i, a \in A_i\)
- symmetric
- transitive: \(aRb,bRc\), \(a,b\in A_i\ \ b,c \in A_j\). because \(A_i \cap A_j=\emptyset(i \neq j)\), so \(i=j\)
4a48fe0446513dfdb3c3cc67cb93c5e7.png
\(|A|=n\), how many different equivalence relations on the set \(A\) are there
Consider the partition of A. \(\sum_{k=0}^n S(n,k)\)
Operation of equivalence relations
\(R_1,R_2\) is equivalence relation, \(R_1 \cup R_2\) is not
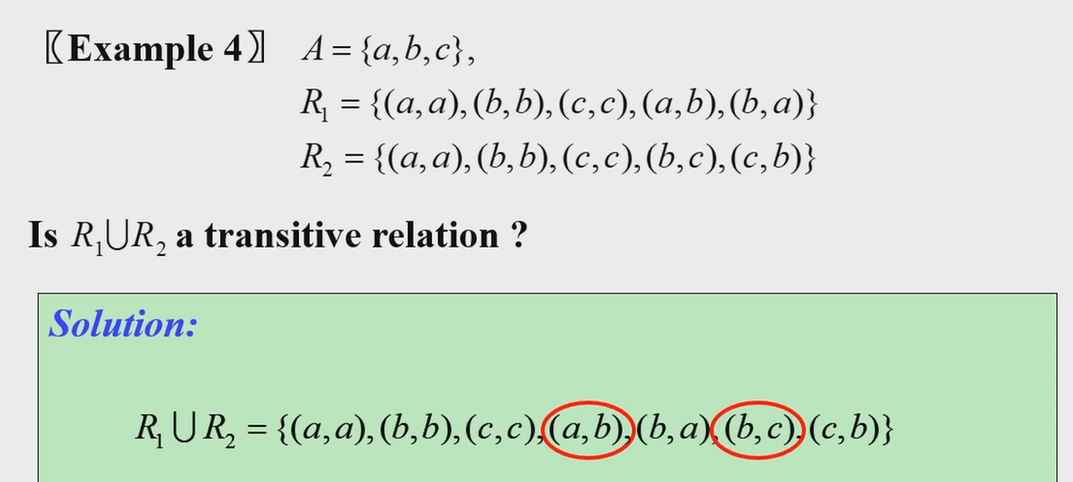
因为不满足Transitive, 对\(R_1 \cup R_2\) 再跑传递闭包就可以
Partial Orderings
a reflexive,antisymmetric and transitive relation is a partial order.
- 验证是partial order,前两项容易,注意transitive relation要枚举3个点
S is a set, R is a partial order on S, \((S,R)\) is called a poset
The elements a and b of a poset \((S, \leq)\) are called comparable if either \(a \leq b\) or \(b \leq a\). (这里的≤代表抽象的大小关系,不是实数的比大小)
If \((S, \leq )\) is a poset and every two elements of S are comparable, S is called a totally ordered or linearly ordered set, or a chain.
Hasse Diagrams
先把偏序关系表示成有向图,根据传递性去掉不需要的边。再分层画出节点,去掉箭头。

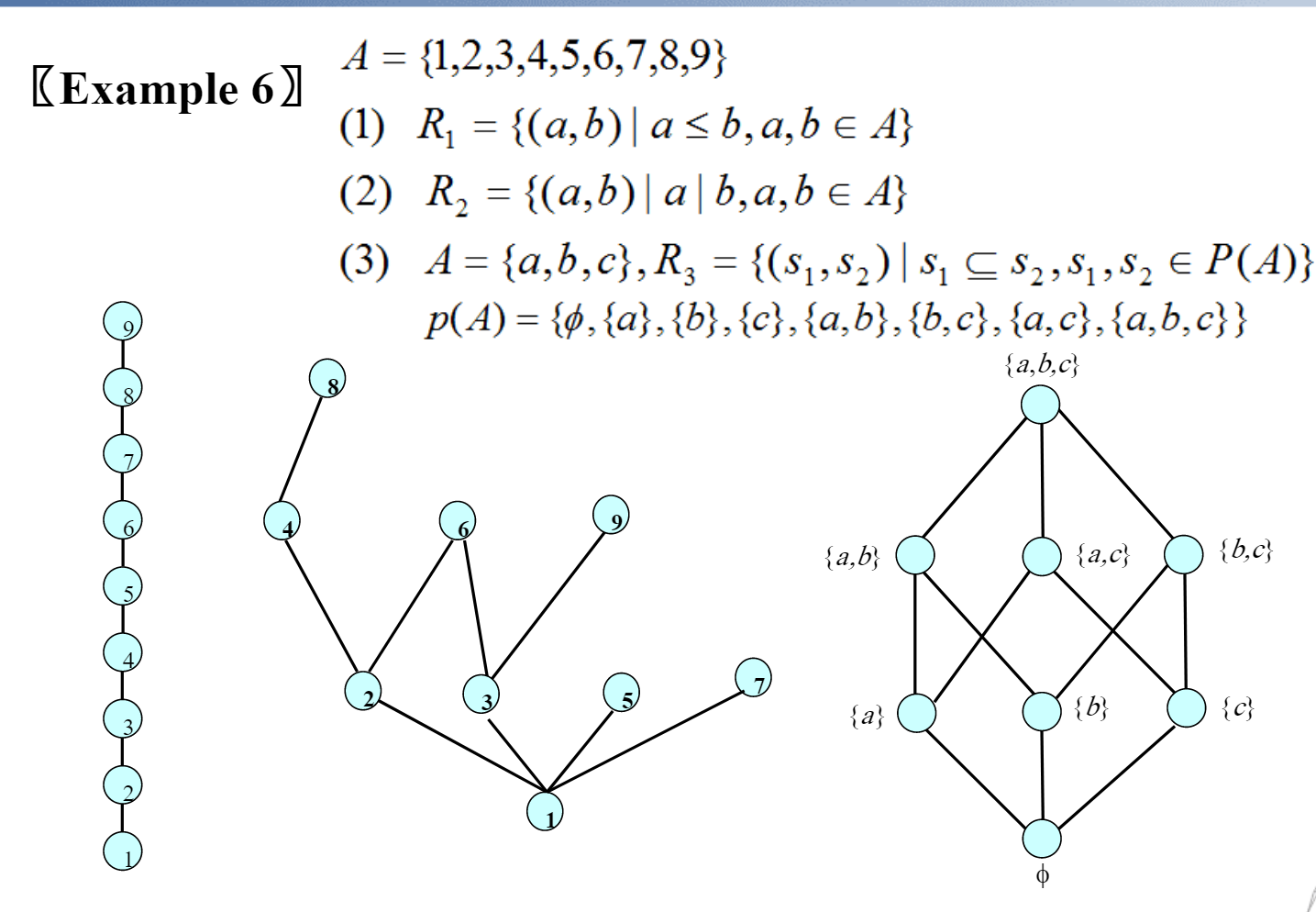
画\((A,|)\)的Hasse diagram,可以不必用通用的方法
- 如果有1,则1在最底部
- 接下来一层是质数
- 依次放上质数的倍数
Chain and antichain
A subset of a poset is called a chain if every two elements of this subset are comparable.
A subset of a poset is called an antichain if every two elements of this subset are incomparable
Dilworth's theorem:
every finite poset can be partitioned into k chains, where k is the largest number of elements in an antichain in this poset
Special Elements
-
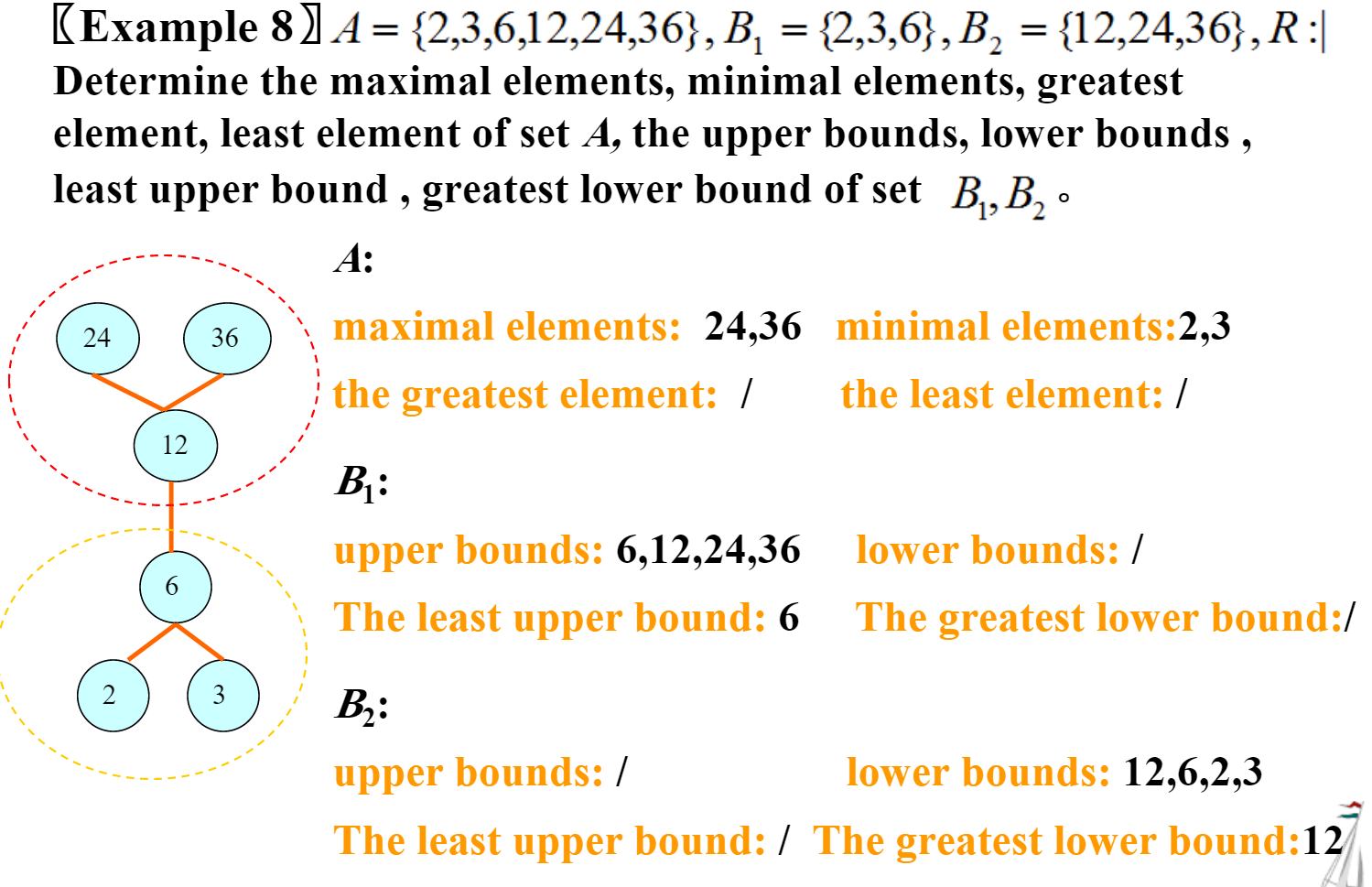
maximal element \(m\): 不存在\(a \in S,a \geq m\) (可能有多个,也可能不存在) (top element of Hasse diagram)
-
minimal element: (bottom element of Hasse diagram)
-
greatest element: \(\forall a \in S,m \geq a\) (唯一)
-
least element: (唯一)
-
upper bounds: for \(A \subseteq S\), \(\existssss a, \forall b \in A, a \geq b\), then \(a\) is upper bound of \(A\)
- least upper bound(lub)
-
lower bounds
- greatest lower bound(glb).
Lattice
a poset is called a lattice if each pair of elements have a glb and lub.
every totally ordered set is a lattice
\((Z^+,|)\) is a lattice. (glb=两个数的最大公因数,lub=最小公倍数) \((P(S),\subseteq)\) is a lattice (取并集、交集)
Well-ordered set
a well-ordered set is a poset that every nonempty subset of A has a least element. a well-ordered set is a totally ordered set.(choose subset of size 2)
mathmatical induction(见Section 5)