ICS Chapter 1 3
Chapter 1
(1.3.1)The notion of Abstraction
hardware/software
(1.5)Two important ideas:
-
All computers are capable of computing exactly the same things if they are given enough time and enough memory.
-
It is necessary to transform our problem from the language of humans to the voltages that influence the flow of electrons.(language of computer)
- Problem:ambiguity of natual languages
- Algorithm: a step by step procedure, each procedure have 3 properties: (离散数学中讲过)
- effective computability:each step can be carried out by a computer
- definiteness:each step is precisely defined
- finiteness:the procedure terminates after a finite period of time.
- Programming Language
- high level: Python,C++...
- low level: Assembly
- Compiler: High-level Lang. -> Intermediate Form -> ISA
- ISA: Instruction Set Mechanism
- opcodes: operations the computer can perform
- data types: acceptable representations for operands
- addressing modes: mechanisms that the computer can use to figure out where the operands are located
- Microarchitecture: is the digital logic that allows an instruction set to be executed. (implementation) ISA是抽象的指令(类似于接口),而microarchitecture是搭建电路实现这些指令
- Logic Gates
- Circuits
从最顶层的Problem到最底层的circuits,就是从具体到抽象
Chapter 2(重点)
Integer representation
- Signed Magnitude 原码
- 1's Complement 反码
- 2's Complement 补码
补码转原码: 取反+1
补码加法: 符号位也参与运算,符号位的进位不要管
范围\([-2^{\color{red}n-1},2^{n-1}-1]\)
不同长度补码的转换:正数前面补0,负数前面补1 (有符号拓展,SEXT)
(HW1 2.17):0101+110=0101+1110=0011=3
溢出(overflow): 用二进制判断: 符号位前的进位和符号位后的进位不同,则溢出
(HW1 2.20)
16进制补码:如果是正数,直接转16进制,前面加x. 如果是负数,那么就以转完16进制后的长度(4*k)做补码
(HW2 2.48)
Floating point
32-bit(float)
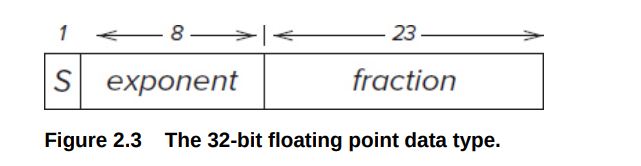
(16bit: 1 / 5 / 10 64bit: 1/11/52)
- 8位的exponent是无符号的,范围是\([0,255]\)
- 23位的
fraction
当\(1 \leq \text{exponent} \leq 254\) (Normalized Form)
\(\boxed{N=(-1)^S\times 1.\text{fraction}\times 2^{\text{exponent}-127},1 \leq \text{exponent} \leq 254}\)
绝对值最小 \(1.0000...0\times 2^{-126}=2^{-126}\)
绝对值最大 \(1.1111\dots 1\times 2^{127}\approx 2^{128}\)
(2.40) 1 10000000 10010000000000000000000
\((-1)^1\times 1.1001\times 2^{128-127}=-3.125\)
当\(\text{exponent}=255\) (infinities)
用来表示无穷. 如inf就是exponent=255,fraction全0. 如果exponent=255,fraction不是全0,就是NaN
当\(\text{exponent}=0\) (subnormal numbers)
\(N=(-1)^S\times 0.fraction \times 2^{-126}\)
最大\(0.111\dots1\times 2^{-126}=(1-2^{-23})\times 2^{-126}\)
最小\(0.000\dots 1\times 2^{-126}=2^{-149}\)
注意这里是0.fraction,而不是Normalized Form中的1.,且指数换成了-126. 去掉要求的1,这样可以表示的指数范围就从-127变到了-149。
Digital Logic Structures
Transitors
PMOS \(U_G-U_S<-1.2V\)导通 一般作上管(和\(U_S=1.2V\)相连,此时若\(U_G=0\)则导通)
N-type \(U_G-U_S>1.2V\) 一般作下管(接地\(U_S=0\),此时若\(U_G=1.2V\)则导通, \(U_G=0\)则断路
Gates
NOT Gates
横线代表正极,三角形代表接地
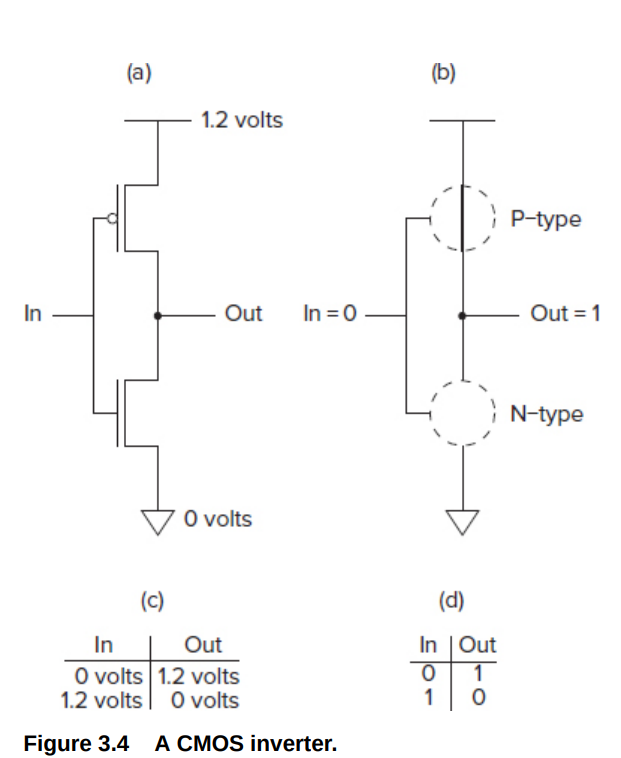
NOR/OR
OR=NOR+NOT,所以只需要看左边的NOR
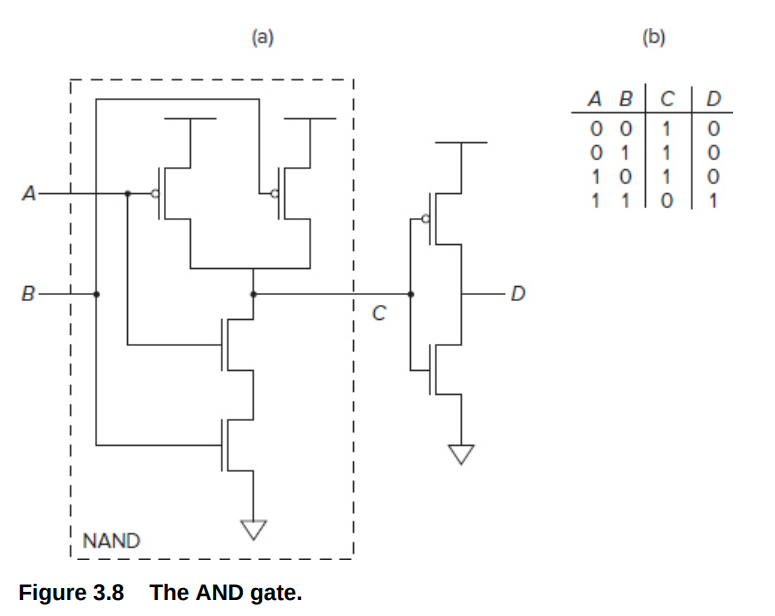
NOR,当且仅当输入是两个0的时候为1, 因此上面用两个P-type串联,仅两个都是0的时候导通,输出为1。下面用两个N-type并联,只要有1个为0的时候就导通接地,输出为0。
上半部分选择什么时候高电势(1),下半部分选择什么时候接地(0) 串联代表"与" 并联代表"或"
如果是多个输入,只需要把多个输入串联起来或者并联起来即可。
NAND/AND
同理对于NAND,只要输入有1个0,输出就为1,所以上面用两个P-type并联, 下面用两个N-type串联
Combinatorial Logic Circuits
对前面半导体的结构进行进行封装,就得到了常见的逻辑门,符号如下
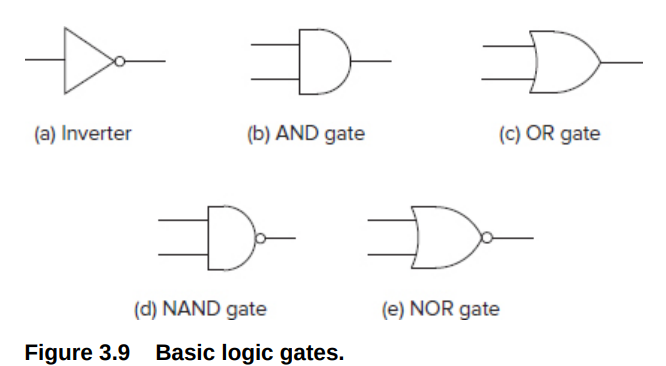
NOT Gate有时也简化成一个小圆圈.
表达式: \(A+B\) 表示\(A\) OR \(B\). \(AB\) 表示 \(A\) AND \(B\) \(\bar{A}\) 表示 NOT \(A\)
Decoders
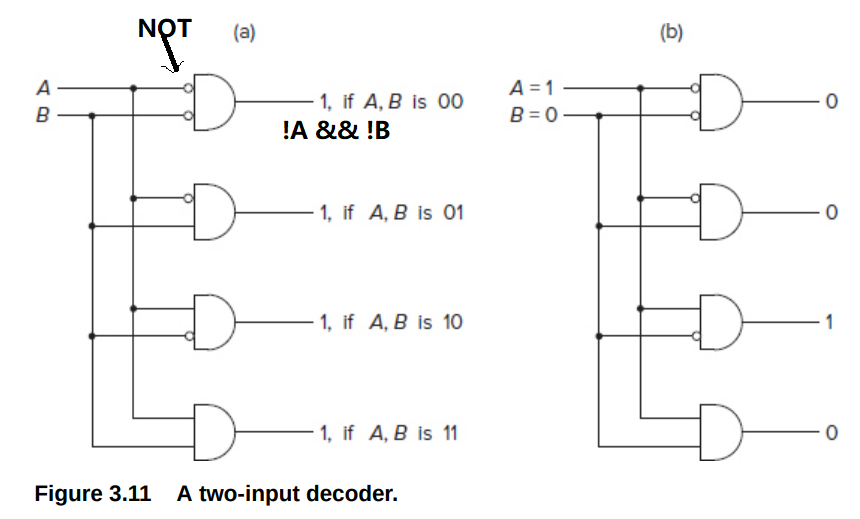
用AND和NOT组成(注意前面的空心圆圈代表NOT)
分类所有输入的组合。可用于解析opcode
MUX
- \(2^n\) inputs, 1 output, n select lines
通过S来选择对应的输入
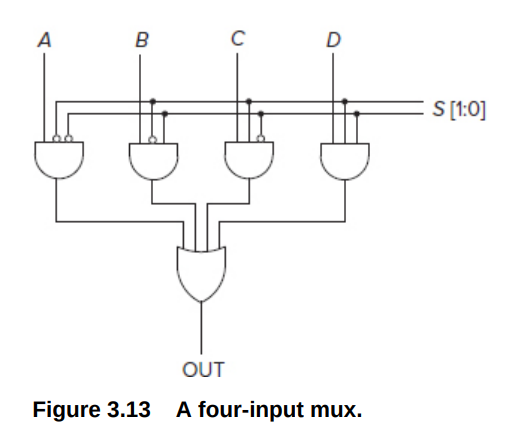
S=00,01 10 11 分别输出A,B,C,D
1-bit adder
本质上也是decoder,对输入的\(A_i,B_i,C_{i-1}\)输出对应的\(S_{i},C_{i}\). 如果为1就连向对应的输出
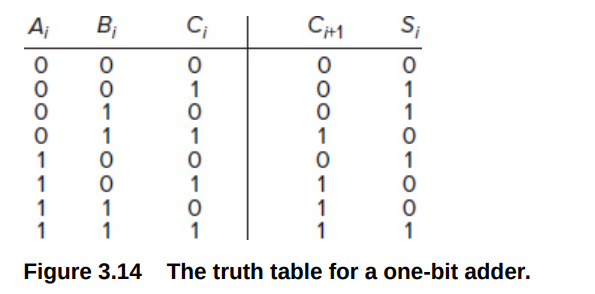
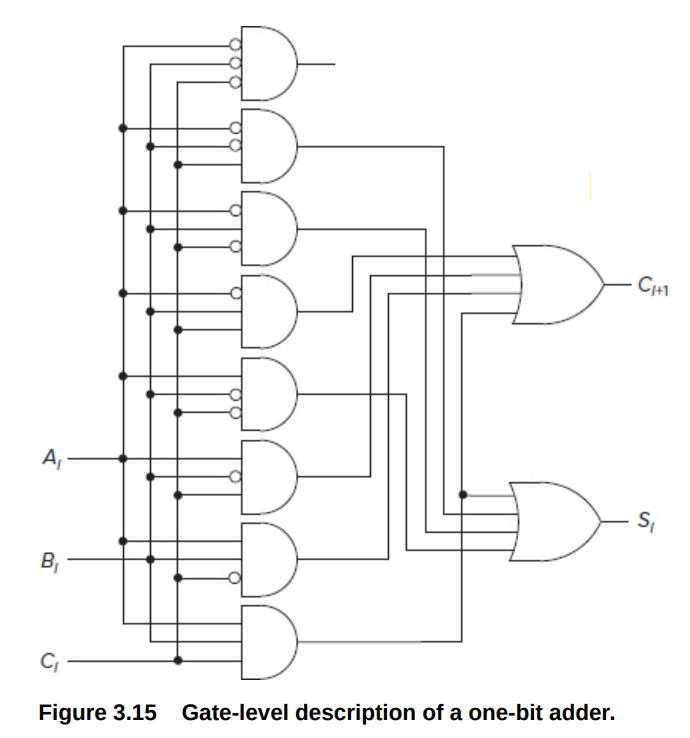
从上到下对应000,001...111
The Programmable Logic Array (PLA)
对1-adder进行进一步抽象, 相当于decoder+内部自定义连接+一系列or gates
这种思路很重要。对于一些过程,如比较,加法等,我们不需要关心实现思路,只需要列出真值表然后用PLA解析即可。对于n-bit输入,m-bit的输出, 对于每一个输入\(x\)(共\(2^n\)个), 对应输出\(y\), 把\(x\)对应的AND Gate 连向 \(y\)中为1的bit对应的OR Gate
Patt在这本书中强调的是更简单的去设计逻辑电路,而不是追求用更少的逻辑门
HW2 3.3
Storage Elements
R-S latch
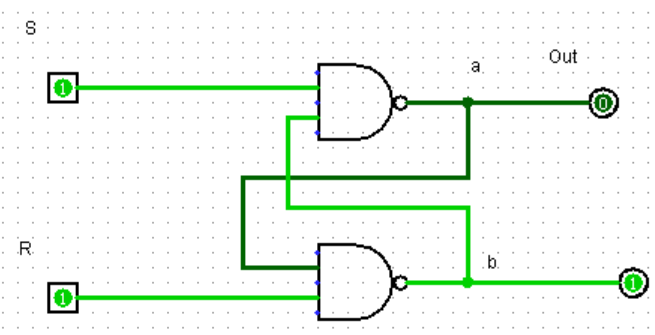
R = S = 1:hold current value in latch (Out can be 0 o)
S = 0, R=1:set value to 1 (set)
R = 0, S = 1:set value to 0 (reset)
R = S = 0(•Don’t do it!)
•both outputs equal one
•final state determined by electrical properties of gates
Gated D latch
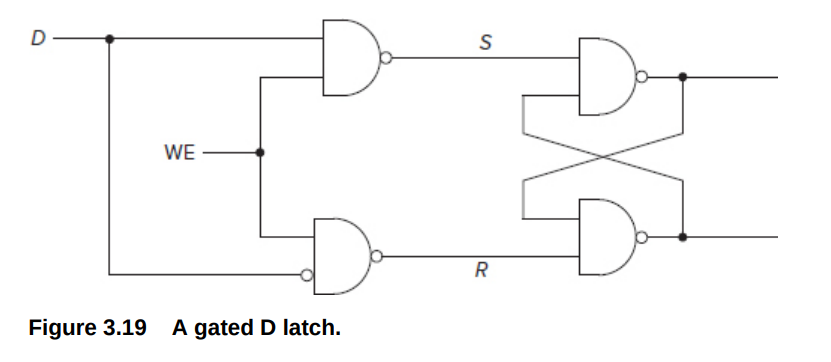
WE=0, S=R=1 no matter what D equals to(Write is not enabled, store the previous state)
WE=1(Write Enable, Set the value to D)
D=1,S=0,R=1,Out=1 D=0,R=0,S=1,Out=0
Prevents S=R=0
Memory
address space:the total number of uniquely identifiable locations addressability: The number of bits stored in each memory location
\(n\) bits of address, \(2^n\) locations in the address space. \(A\)代表地址 \(D_l[2:0]\)代表要写的值 \(D[2:0]\)代表要读的值
每一行对应一个地址,每个gate D latch存储一位二进制
decoder用于选择对应的行
mux用于读出latch里面的值
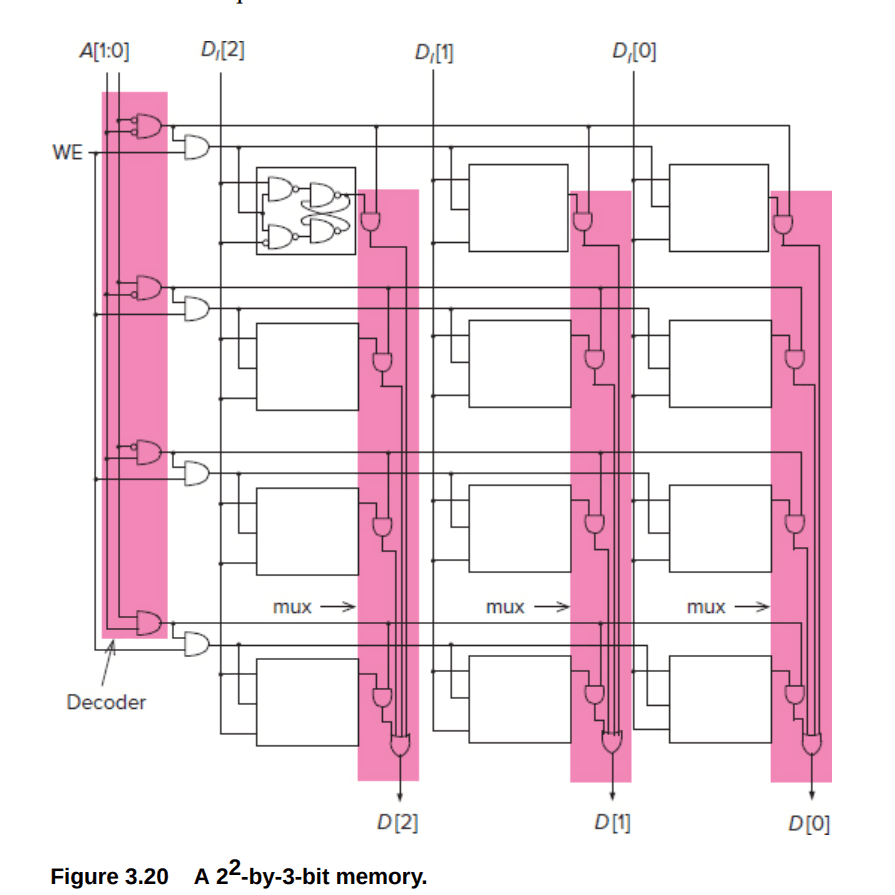
左边第一列是用来选写的行 其余是用来的
Finite State Machines
Synchonous Finite State Machines
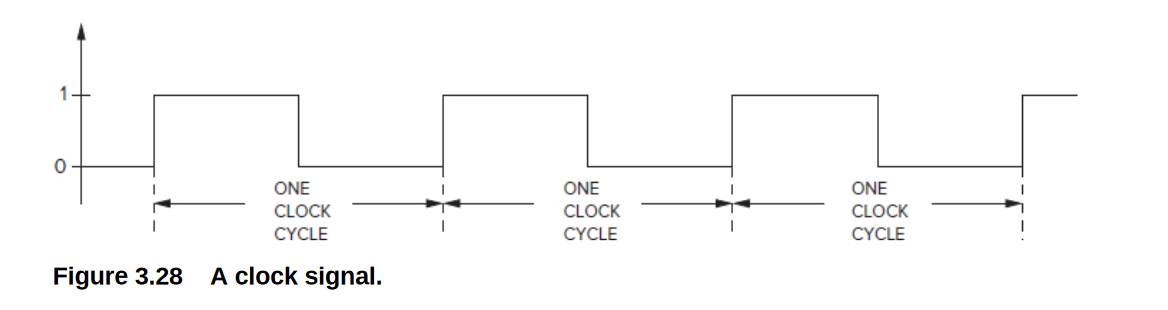
the clock is a signal whose value alternates between 0 and 1.
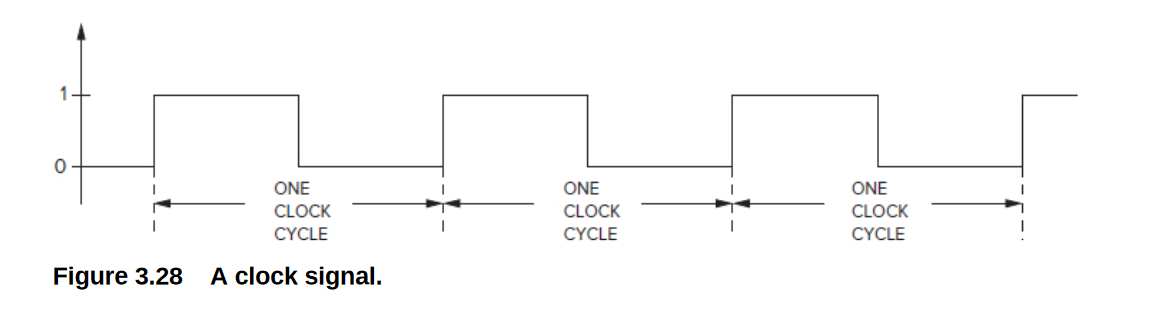
synchronous:the state transitions take place, one after the other, at identical fixed units of time
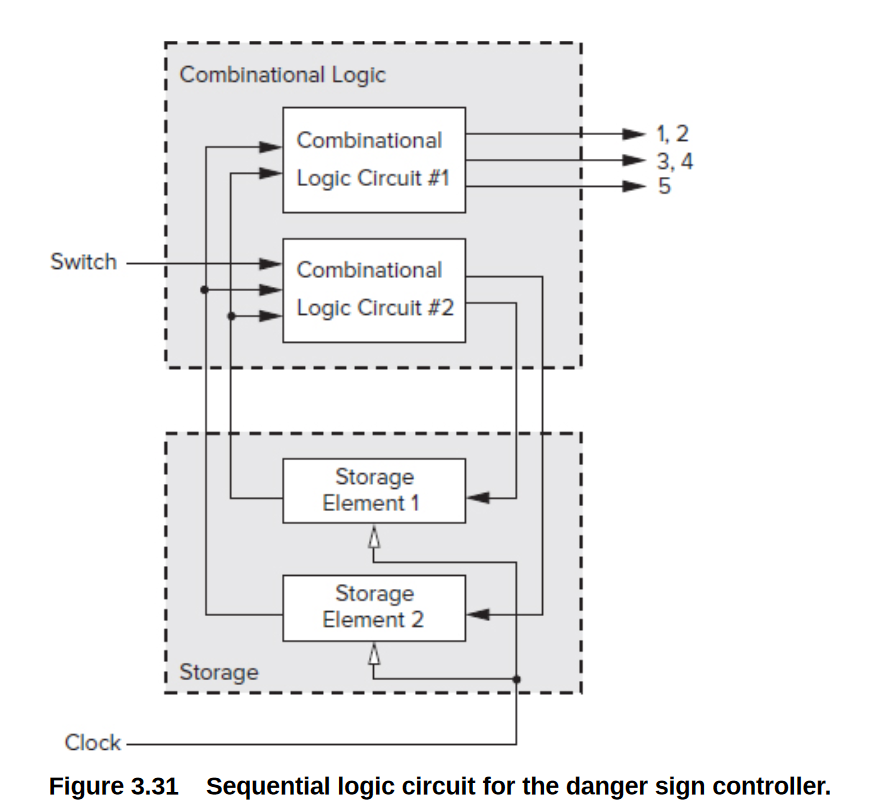
原理:Combinational Logic Circuit #1是输出模块
Combinational Logic Circuit #2 本质上是一个PLA, 输入是状态机的当前状态和开关Switch,输出的是状态机的下一个状态,状态编码存储在Storage里
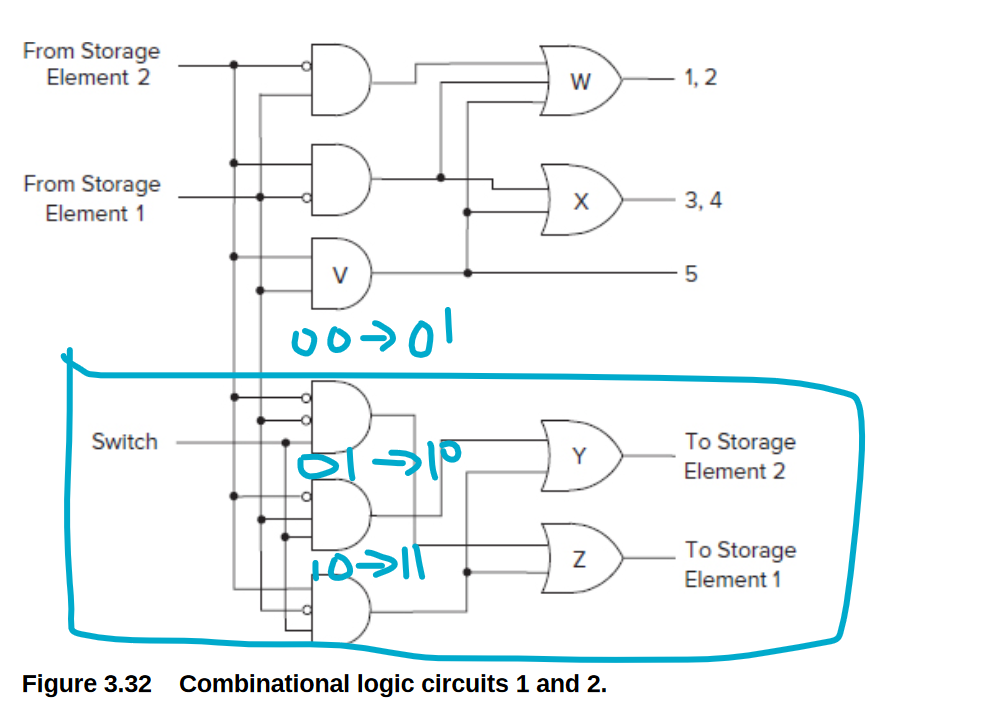
把状态机的变化关系(带时序的真值表) 画成电路
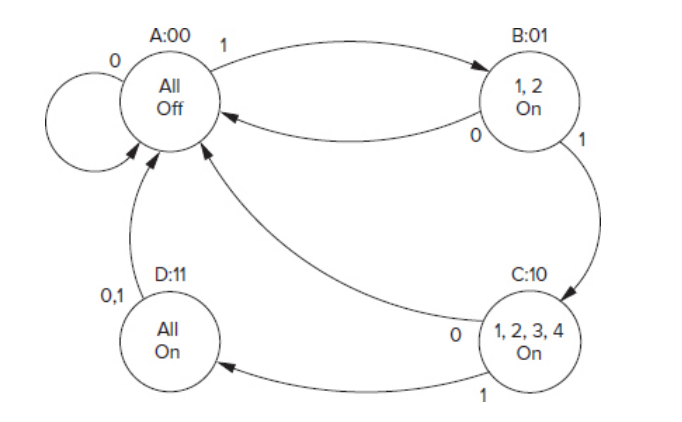
状态机: - 点上要写状态\(S\) - 线上写输入\(X\)表示状态转移 - 输出如果和输入无关,就写在点上。否则写在输入后面
Flip-Flop
防止状态快速变化
We do not want the input to the storage elements to take effect until the end of the current clock cycle.
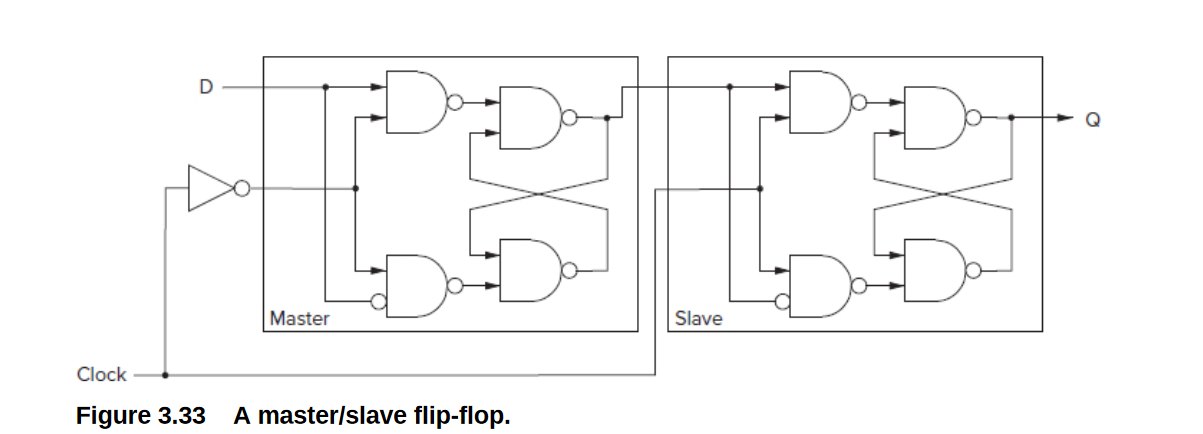
原理:
- 在时钟周期的前一半(A),Clock=1, Master不可写,Slave可写, Master存储的状态\(S_n\)被写入Slave
- Combinatorial Logic根据Slave的状态\(S_n\)计算\(S_{n+1}\)
- 在时钟周期的后一半(B),Clock=0,Master可写,Slave不可写,新的状态\(S_{n+1}\)被写进Master, 下一个时钟周期再进入Slave
Master起到了缓存下一个状态的作用